International Board Group
Get in Touch With Us
Office Address
Bank of the West Tower - 500 Capitol Mall, Sacramento, CA 95814
Email Address
Telephone
(650) 250 - 5845
AI Innovations in Agriculture: Pioneering a Sustainable Future
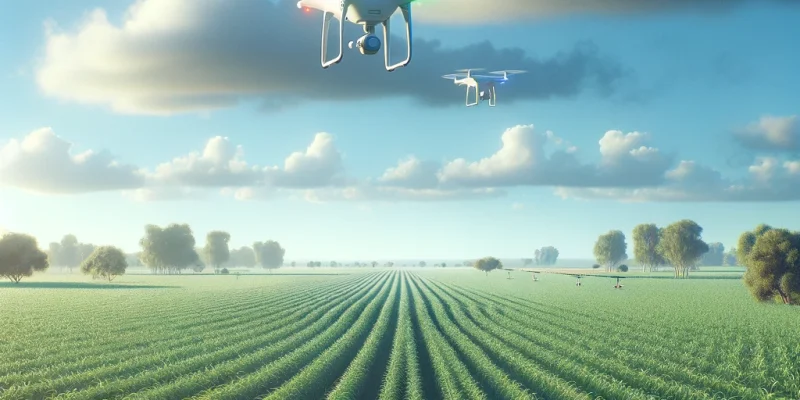

Agriculture, a cornerstone of human civilization, is undergoing a transformative shift, propelled by the challenges of productivity, global food security, and resource conservation. As the world population is projected to reach 9.3 billion by 2050, the Food and Agriculture Organization highlights the need to increase food production by 60%. Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a pivotal technology in revolutionizing farming practices to meet these demands sustainably.
The Growing Role of AI in Modern Agriculture
Market Projections and Impact The AI in Agriculture Market is expected to grow from $1.7 billion in 2023 to $4.7 billion by 2028. This significant growth underscores AI’s role in enhancing agricultural practices through innovations in automated supply chains, product quality checks, and predictive maintenance, among others.
Addressing Key Challenges with AI
Combatting Pests Pests account for approximately 40% of global agricultural productivity losses annually, translating to a financial burden of at least $70 billion. AI-driven solutions like Trapview utilize pheromone-based trapping and computer vision to identify and manage pest populations effectively, enabling farmers to optimize pesticide use and enhance crop yields.
Improving Soil Quality and Irrigation With 33% of Earth’s soil degraded and agriculture consuming 70% of the world’s freshwater, AI applications are crucial in managing these resources more efficiently. Technologies like CropX analyze data from various sources to monitor soil health and automate irrigation systems, significantly reducing water and fertilizer usage while boosting crop output.
Weed Management Weeds significantly impact crop yields and quality. Innovations such as Carbon Robotics’ LaserWeeder use AI-driven computer vision to distinguish weeds from crops, allowing for precise weed control that conserves herbicides and reduces labor costs.
The Transformative Impact of AI on Agriculture
Enhancing Productivity and Sustainability AI innovations are not just solving immediate problems but are also setting the stage for long-term sustainability in agriculture. These technologies enable farmers to maintain higher productivity levels while minimizing environmental impacts, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Economic and Social Shifts The integration of AI in farming is also reshaping economic and social landscapes by reducing the reliance on manual labor and shifting skill requirements within the agricultural workforce. This shift necessitates a focus on reskilling and ethical considerations to ensure that the benefits of AI are distributed equitably.
Ethical Considerations and Future Outlook
Navigating the Risks While AI offers substantial benefits, it also poses risks such as potential job displacement and data privacy concerns. The concentration of ownership might favor large agribusinesses, posing challenges for smaller farms. Therefore, it is crucial to implement thoughtful governance and regulatory frameworks to mitigate these risks and ensure that AI’s benefits are shared across the agricultural sector.
IBG Insights
The integration of AI in agriculture is a promising frontier for enhancing food production efficiency and sustainability. As we harness these technologies, it is imperative to balance innovation with ethical considerations and equitable benefits distribution. Looking ahead, AI’s role in agriculture will continue to expand, offering new ways to meet the world’s food needs sustainably and responsibly.
By embracing AI, the agricultural sector can navigate present challenges and future uncertainties, ensuring resilience and productivity in a rapidly changing world. The journey of AI in agriculture is just beginning, and its full potential remains to be seen in the coming decades.
More insights into the boardroom
Get In Touch
- [email protected]
- (650) 250 - 5845
Corporate Office
500 Capitol Mall, Sacramento, CA 95814